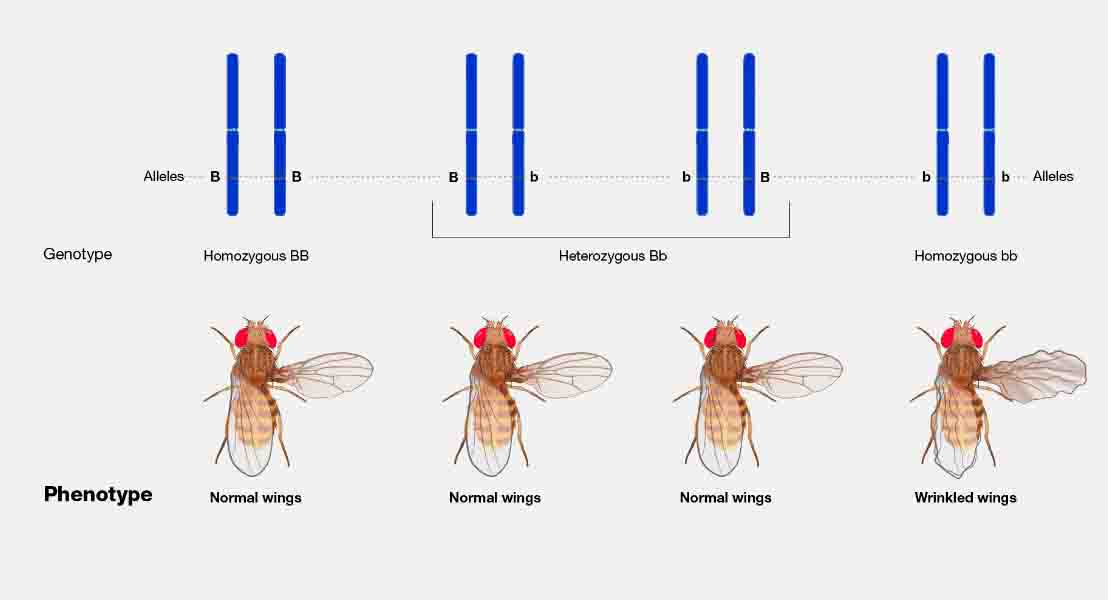
Phenotype Definition
A phenotype is the physical expression of DNA. In contrast, the genotype is the chemical makeup of DNA that causes a particular phenotype. DNA is first transposed into RNA, a slightly different information molecule, which can then be translated into a protein. Phenotypes are caused by the interactions of the many different proteins created by DNA.
This process can get incredibly complicated. Even in the lowest lifeforms there are thousands of genes, creating thousands of different proteins. These proteins interact in complex ways with each other and the environment, allowing the organism to obtain energy from nutrients.
In a simple sense, each gene can produce a single protein. This protein can take several different forms, based on the different alleles in the population. Some of these forms will be functional, while other forms will be less functional or not work at all. If a trait is controlled by a single protein, the genotype that the animal receives for that protein will determine if that trait is adaptive or detrimental in the pursuit of reproduction.
For instance, people with cystic fibrosis (CF) have a mutation in the gene that produces a protein specific to transporting chlorine molecules across membranes. Because their genotype contains a non-functional mutation, the protein created does not function properly. Thus, they have a non-functional phenotype, causing many health problems.
Examples of Phenotype
Melanin
Melanin is a molecule produced by many animals. It is known as a pigment, or a molecule that gives tissue a dark color. In humans, varying levels of melanin in the hair, eyes, and skin are what cause such a wide variety of appearances in the world.
While there are many genes that control the distribution of melanin, there are only a few genes responsible for its production. That is why, in any population around the globe, individuals can be found that produce no melanin at all, a condition known as albinism.
Those with albinism, regardless of their race or parent’s phenotypes, lack the ability to produce melanin. Without the pigment in their system, their hair and skin appears white, and eyes usually a shade of pink. All populations contain albinism because the pool of genes responsible for producing melanin is large, and a mutation in any of them can disrupt the entire process.
Although mutations are rare, when enough people are reproducing, the trait will appear. However, because of the decreased protection from the sun’s rays, many with albinism are subjected to a variety of skin and eye cancers. This may explain why albinism is usually seen in only a small portion of the population.
Animals also experience albinism, as the pathways that produce melanin in them are much the same as in humans. In fact, albinism has been documented in most mammals. All mammals use melanin as a pigment. Other groups of animals use different pigments, with different mechanisms for making those pigments.
Albinism is also possible in those animals, if the genes that produce the pigmented phenotype get disrupted. Sometimes these mutations are selected for, as in the case of winter animals, which often show partial albinism in their coats, allowing them to blend in and absorb more solar energy.
Mendel’s Peas
Gregor Mendel is most known for his contributions to genetics. As a friar at a Germany abbey, Mendel studied the phenotypes of peas. Mendel was particularly interested in the phenotype ratio between the offspring. Mendel noticed that when he bred yellow peas with green peas, sometimes the offspring would be half yellow and half green, and sometimes the offspring would be all yellow.
Mendel concluded that each pea carries two forms of the gene for color. We now call these alleles, and we know why Mendel’s peas would produce offspring in different ratios of colors. In the following Punnett squares, each square represents a potential offspring between the parents listed on the outside of the larger square. Remember, each parent gives one allele to each offspring.
The phenotype of color in peas is caused by a gene that produces the yellow pigment. Without this pigment, the chloroplasts in the pea pod give it a green color. Each organism contains two alleles for the gene, one received from each parent. If an organism receives even one allele that can produce the yellow pigment, the pea pod will be yellow.
If however, neither of the alleles can produce the yellow pigment, the peas will appear green. The yellow allele is known as the dominant allele, because only one will cause the yellow phenotype, or outward appearance. The green allele is the recessive allele, because you need two green alleles in an individual to produce
Related Biology Terms
- Transpose – Staying in the language of DNA, to transpose is to copy DNA into an RNA molecule that serves as the reciprocal of the DNA.
- Translate – Switching to the language of proteins, RNA is then converted to a chain of amino acids by reading the RNA in groups of three known as codons.
- Phenotypic Ratio – The ratio of one phenotypes to the others in a population, which is different than the genotypic ratio.
- Allele – A specific form of a gene, of which you will receive one from each parent, giving you two alleles for every genotype which work together (or against each other) to produce the phenotype.
FAQ’s
A phenotype is the observable physical or biochemical characteristics of an organism, resulting from the interaction between its genotype and the environment. It includes traits such as eye color, height, and behavior.
A phenotype is determined by both genetic and environmental factors. Genes provide the instructions for the development of certain physical traits, while the environment can influence gene expression and modify the phenotype.
Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, while phenotype refers to its observable characteristics. Genotype determines the potential for certain traits, while phenotype is the result of the interaction between genotype and environment.
Phenotype is used in genetics to study the inheritance of traits and to determine the underlying genetic factors. By comparing the phenotypes of individuals with known genetic differences, researchers can identify the genes responsible for certain traits and determine their mode of inheritance. This information can be used in genetic counseling and to develop treatments for genetic disorders.