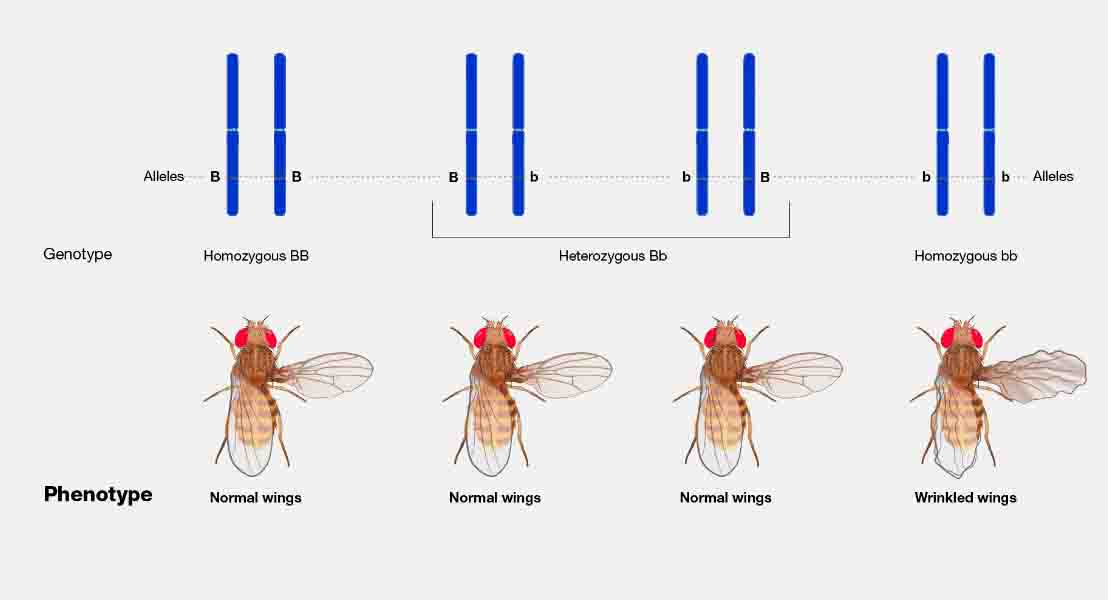
Phenotype
Phenotype Definition A phenotype is the physical expression of DNA. In contrast, the genotype is the chemical makeup of DNA that causes a particular phenotype. DNA is first transposed into RNA, a slightly different information molecule, which can then be translated into a protein. Phenotypes are caused by the interactions of the many different proteins … Read more